This page originally appeared on @THEU & Adapted from NASA Webb Space Telescope.
“We only know of a handful of kilonovas with any certainty, and this is only the second one for which we have such detailed spectral information” said Tanmoy Laskar, assistant professor at the University of Utah, of the first detection of we have of heavy element from a star merger.

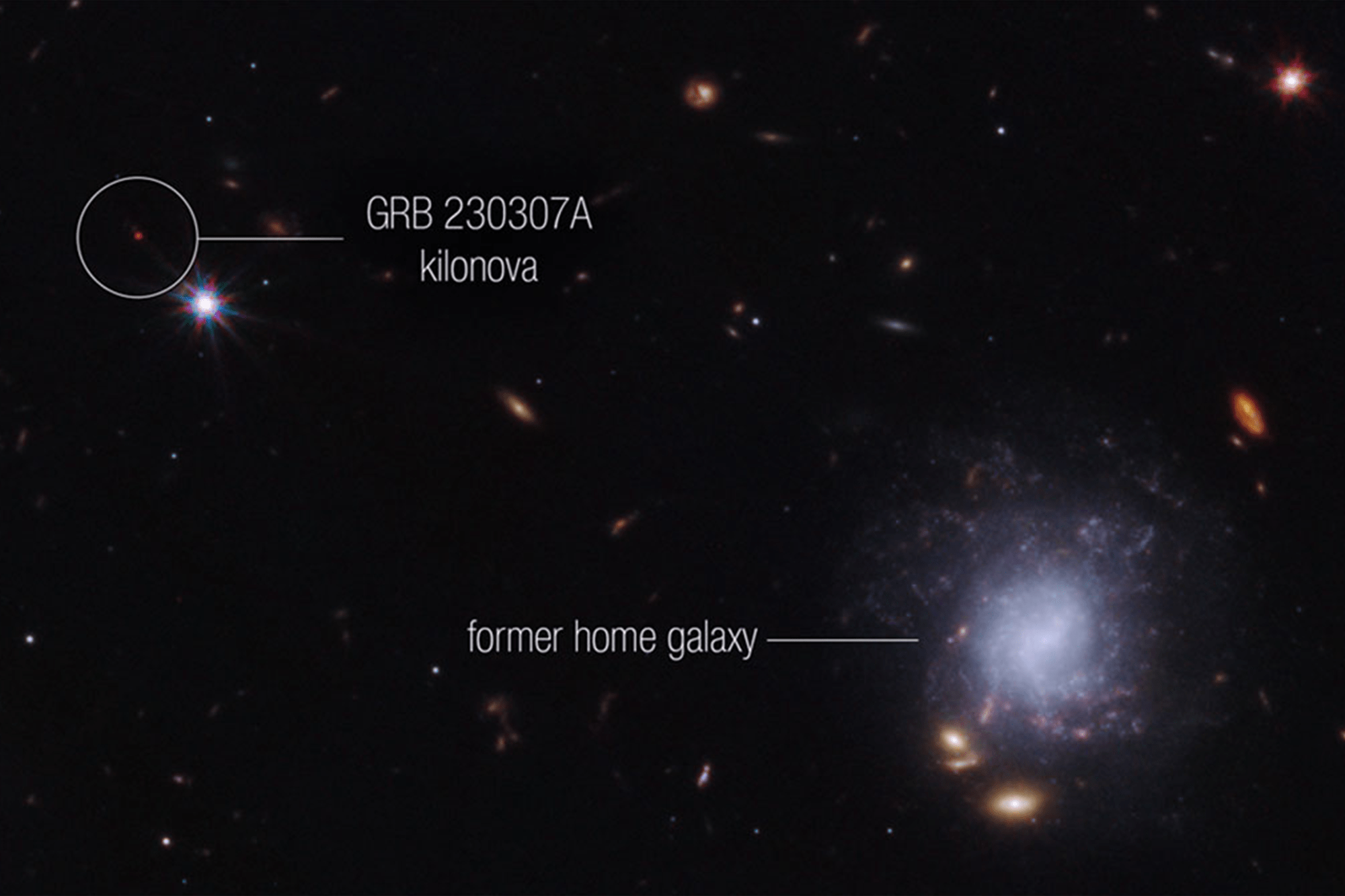
The neutron stars were kicked out of their home galaxy and traveled the distance of about 120,000 light-years, approximately the diameter of the Milky Way galaxy, before finally merging several hundred million years later.
Tanmoy Laskar and colleagues has used multiple space and ground-based telescopes, including NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope, and NASA’s Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory, to observe an exceptionally bright gamma-ray burst, GRB 230307A, and identify the neutron star merger that generated an explosion that created the burst. Webb also helped scientists detect the chemical element tellurium in the explosion’s aftermath.
“Just over 150 years since Dmitri Mendeleev wrote down the periodic table of elements, we are now finally in the position to start filling in those last blanks of understanding where everything was made, thanks to Webb,” said Andrew Levan of Radboud University in the Netherlands and the University of Warwick in the UK, lead author of the study.
While neutron star mergers have long been theorized as being the ideal “pressure cookers” to create some of the rarer elements substantially heavier than iron, astronomers have previously encountered a few obstacles in obtaining solid evidence.
Kilonovas are extremely rare, making it difficult to observe these events. Short gamma-ray bursts (GRBs), traditionally thought to be those that last less than two seconds, can be byproducts of these infrequent merger episodes. In contrast, long gamma-ray bursts may last several minutes and are usually associated with the explosive death of a massive star.
The case of GRB 230307A is particularly remarkable. First detected by NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope in March, it is the second brightest GRB observed in over 50 years of observations, about 1,000 times brighter than a typical gamma-ray burst that Fermi observes. It also lasted for 200 seconds, placing it firmly in the category of long duration gamma-ray bursts, despite its different origin.
“This burst is way into the long category. It’s not near the border. But it seems to be coming from a merging neutron star,” added Eric Burns, a co-author of the paper and member of the Fermi team at Louisiana State University.
Read the full article by Lisa Potter in @THEU
